Geometry Calculators
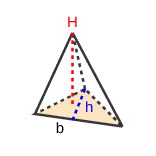
Interactive visuals for areas, perimeters, surface areas, and volumes across 2D/3D shapes.
Open GeometryTrig Basics (sin / cos / tan)
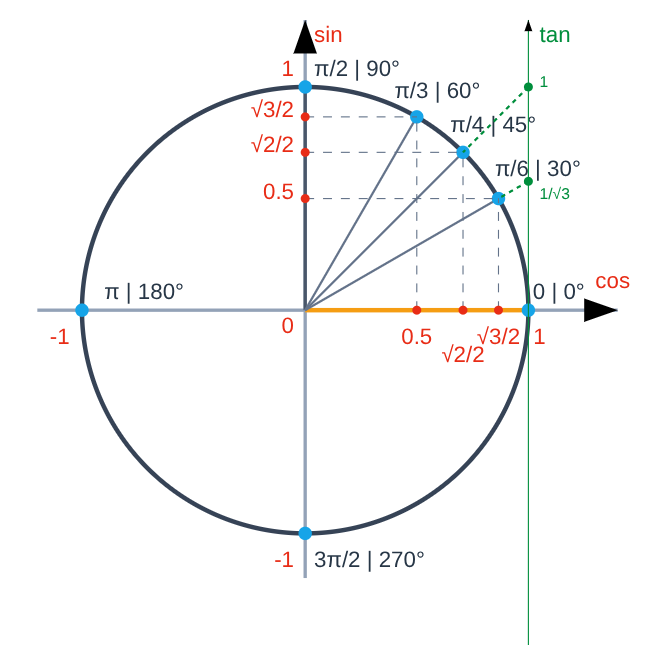
Intro trigonometry: ratios, unit circle intuition, and the foundations before identities and graphs.
Open Trig BasicsMore Coming Soon
Unit converters, real-world guides, quizzes, and advanced topics are on the roadmap.
See the vision